| |
p53 Information
p53 isoforms
p53 partners |
mdm family
mouse models
ASPP family
|
p53 isoforms
Alternative splicing of the human p53 gene has been first described by Matlashewski et al. in 19 !è and later by Flaman et al. in 1996 [Matlashewski et al., 1987; Flaman et al., 1996]. In mouse, an alternative splice changes the carboxy-terminus of the protein [Arai et al., 1986]
Untill 2005, these observations were not fully apreciated. Recent studies using more sensitive methodology has uncovered at least 8 isoforms, the function of which remains unknown [Courtois et al., 2002; Bourdon et al., 2005; Rohaly et al., 2005; Ray et al., 2006].

|
Human p53 isoforms: Click each isoform for more information
|
 |
| Wild type full length p53 (393 residues) |
 |
| p53 beta: alternative splice of intron 9 |
 |
| p53 gamma: alternative splice of intron 9 |
 |
| Delta 40 (also known as p44, p47 or delatN p53: Initiation of translation at codon 40. |
 |
| Delta 40 beta: Initiation of translation at codon 40 + alternative splice of intron 9 |
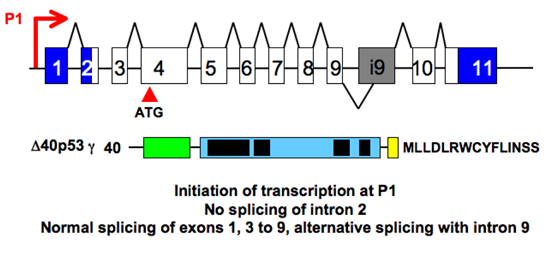 |
| Delta 40 gamma: Initiation of translation at codon 40 + alternative splice of intron 9 |
 |
| delta 133: initiation of translation at codon 133 |
 |
| delta 133 beta: initiation of translation at codon 133 + alternative splice of intron 9 |
 |
| delta 133 gamma: initiation of translation at codon 133 + alternative splice of intron 9 |
 |
| delta p53: alternative splicing between exon 7 and 9. The protein miss 66 residues including Highly Conserved Domain V. |
References
- Arai N, Nomura D, Yokota K, Wolf D, Brill E, Shohat O, Rotter V (1986) Immunologically distinct p53 molecules generated by alternative splicing. Mol Cell Biol 6: 3232-3239.
- Bourdon JC, Fernandes K, Murray-Zmijewski F, Liu G, Diot A, Xirodimas DP, Saville MK, Lane DP (2005) p53 isoforms can regulate p53 transcriptional activity. Genes Dev 19: 2122-2137.
- Courtois S, Verhaegh G, North S, Luciani MG, Lassus P, Hibner U, Oren M, Hainaut P (2002) DeltaN-p53, a natural isoform of p53 lacking the first transactivation domain, counteracts growth suppression by wild-type p53. Oncogene 21: 6722-6728.
- Flaman JM, Waridel F, Estreicher A, Vannier A, Limacher JM, Gilbert D, Iggo R, Frebourg T (1996) The human tumour suppressor gene p53 is alternatively spliced in normal cells. Oncogene 12: 813-818.
Matlashewski G, Pim D, Banks L, Crawford L (1987) Alternative splicing of human p53 transcripts. OncogeneRes 1: 77-85.
- Ray PS, Grover R, Das S (2006) Two internal ribosome entry sites mediate the translation of p53 isoforms. EMBO Rep
- Rohaly G, Chemnitz J, Dehde S, Nunez AM, Heukeshoven J, Deppert W, Dornreiter I (2005) A novel human p53 isoform is an essential element of the ATR-intra-S phase checkpoint. Cell 122: 21-32.
|
|






